I will introduce the formula for calculating lift height. (The Excel calculation sheet is now ready.) To simplify the formula and explanation, we will assume the following conditions. We will introduce calculation formulas that take these into consideration at a later date.
- Valves will not be considered due to their many types.
- The pump suction side will not be considered, as the calculation formula will be the same as for the discharge side.
Parameters
- Fluid specifications (flow rate, viscosity, etc.)
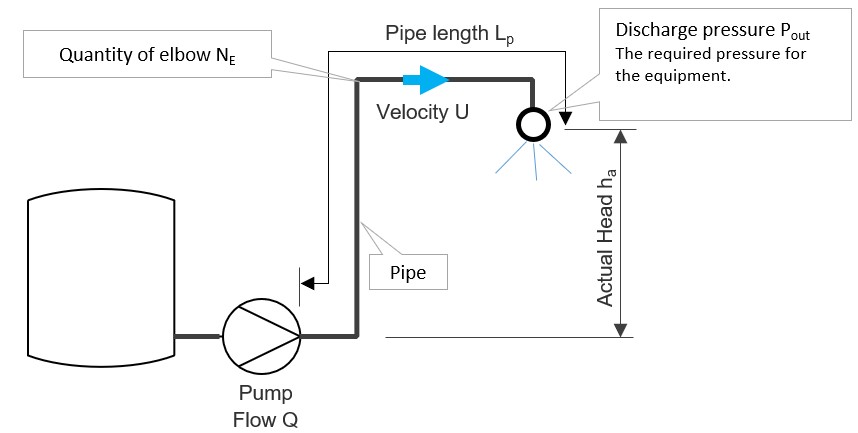
- Mechanical conditions on the discharge side (pipe length, actual lift height, number of valves, number of elbows, required equipment pressure, etc.)流体仕様(流量、粘度など)
Primarily, it is the above two points. However, it is recommended to have a head that allows some margin for future modifications or relocation.
Method
If there are no valves, it becomes simpler and easier to understand as shown in the diagram and formula below. For calculation using the Colebrook-White equation, it requires trial and error, so it is recommended to use the goal seek function in Excel instead of manual calculation. For those who do not understand the goal seek function or want to save the effort of creating an Excel calculation sheet and want to simplify the calculation, you can scroll down to download the Excel calculation sheet.


Excel Calculation sheet
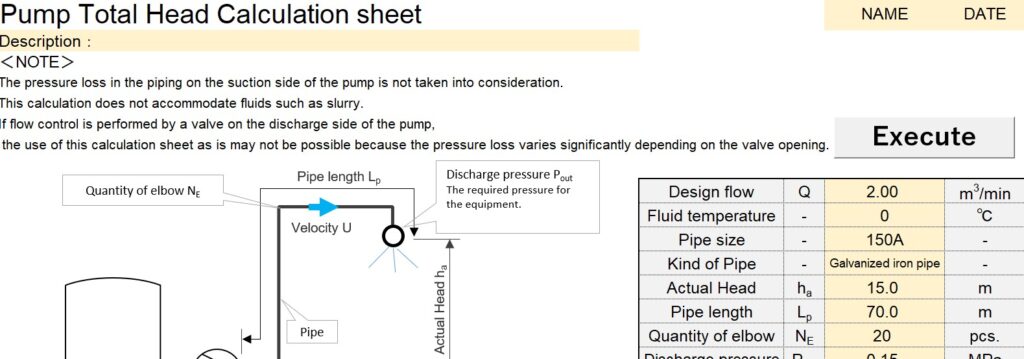
Clicking the link will allow you to download the calculation sheet. As the number of downloads has increased unexpectedly, I am planning to create an Excel sheet for calculating lift height that takes into account the suction side (pressure loss + net positive suction head NPSH).
If you only want to calculate pipe pressure loss, please refer to this article. We have also prepared an Excel sheet that only calculates pipe pressure loss.



コメント